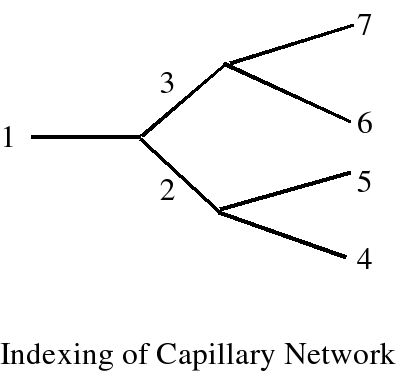
Model represents a network of multilayer segments for pulmonary air-blood exchange.
Description
A full network model is presented for pulmonary air-blood exchange between capillaries and alveolae. It is assumed that capillaries form an ideal binary branching network that can model flow and geometrical heterogeneity of pulmonary blood circulation. Each capillary is surrounded by five cellular or fluid layers and by an alveoli. Overall a single branched segment contains the following layers: capillary, endothelial, interstitial, epithelial, and alveolar layers. The layers are modeled by a system of one-dimensional, time-dependent, non-homogeneous convection-diffusion equations. The source terms of the system can model chemical reactions and species exchange between layers.

Equations
The following equations defines the system
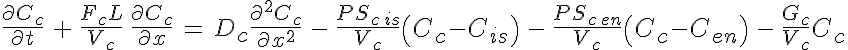
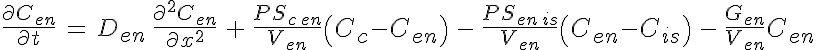
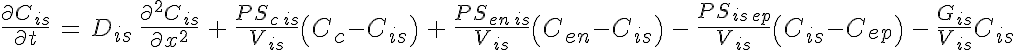
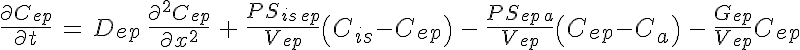
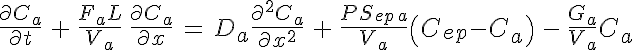
where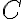 is the species concentration,
is the species concentration,
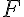 is the volume flow rate,
is the volume flow rate,
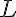 is the segment length,
is the segment length,
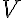 is the volume of layer,
is the volume of layer,
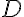 is the coefficient of axial diffusion,
is the coefficient of axial diffusion, 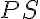 is the product of permeability and surface penetration area,
is the product of permeability and surface penetration area,
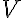 is the reaction consumption coefficient,
is the reaction consumption coefficient, 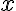 is the spatial coordinate, and
is the spatial coordinate, and 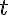 is the time. Index
is the time. Index 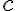 refers to capillary,
refers to capillary, 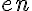 refers to endothelial layer,
refers to endothelial layer, 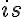 refers to interstitial fluid,
refers to interstitial fluid, 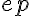 refers to endothelial layer, and
refers to endothelial layer, and 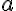 refers to alveoli.
refers to alveoli.
- Download JSim model MML code (text):
- Download translated SBML version of model (if available):
- No SBML translation currently available.
- Information on SBML conversion in JSim
We welcome comments and feedback for this model. Please use the button below to send comments:
Bassingthwaighte JB, Wang CY, and Chan IS.; Blood-tissue exchange via transport and transformation by
endothelial cells. Circ Res 65: 997-1020, 1989.
Bassingthwaighte JB, Chan IS, and Wang CY.; Computationally efficient algorithms for capillary
convection-permeation-diffusion models for blood-tissue exchange. Ann Biomed Eng 20: 687-725, 1992.
van Beek JHGM, Roger SA, and Bassingthwaighte JB.; Regional myocardial flow heterogeneity explained
with fractal networks. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 257: H1670-H1680, 1989.
Please cite https://www.imagwiki.nibib.nih.gov/physiome in any publication for which this software is used and send one reprint to the address given below:
The National Simulation Resource, Director J. B. Bassingthwaighte, Department of Bioengineering, University of Washington, Seattle WA 98195-5061.
Model development and archiving support at https://www.imagwiki.nibib.nih.gov/physiome provided by the following grants: NIH U01HL122199 Analyzing the Cardiac Power Grid, 09/15/2015 - 05/31/2020, NIH/NIBIB BE08407 Software Integration, JSim and SBW 6/1/09-5/31/13; NIH/NHLBI T15 HL88516-01 Modeling for Heart, Lung and Blood: From Cell to Organ, 4/1/07-3/31/11; NSF BES-0506477 Adaptive Multi-Scale Model Simulation, 8/15/05-7/31/08; NIH/NHLBI R01 HL073598 Core 3: 3D Imaging and Computer Modeling of the Respiratory Tract, 9/1/04-8/31/09; as well as prior support from NIH/NCRR P41 RR01243 Simulation Resource in Circulatory Mass Transport and Exchange, 12/1/1980-11/30/01 and NIH/NIBIB R01 EB001973 JSim: A Simulation Analysis Platform, 3/1/02-2/28/07.

