Models two compartments, fluid and air, for a soluble gas passively exchanging between the volumes, V1 liquid, V2 air, with a binding site in V1, forming a closed system. Assumes constant volumes, dry air. Simple model of alveolar-capillary gas exchange.
Description
Simple two compartment model of gas exchange between fluid and gas compartments with binding of gas in
water compartment. Emphasis is on mass exchange as the mass flux of gas across a phase boundary can be
confusing. For this model the compartment volumes and temperature are held constant and the system is
closed so that the total mass in the system is constant.
Amount of CO2 in water compartment = QCO2cap (mol) = CCO2 (mmoles/ml) * VolWater (ml)
Amount of CO2 in air compartment = QCO2air (mol) = pCO2 (mmHg) * VolAir (ml)* (pCO2/760)/(22400 ml/mol)
Example for water with pCO2 of 50 mmHg: Amount Q for CO2 in H2O at 37C (or 310K) =
= AlphaCO2w37 (ml/ml)* (50/760) / 22400
STP O2 and CO2 Solubility Equations from Christmas 2017 Eq 4a and 4b:
Christmas KM and Bassingthwaighte JB. Equations for O2 and CO2 solubilities
in saline and plasma: Combining temperature and density dependences.
J Appl Physiol 122: 1313-1320, 2017.
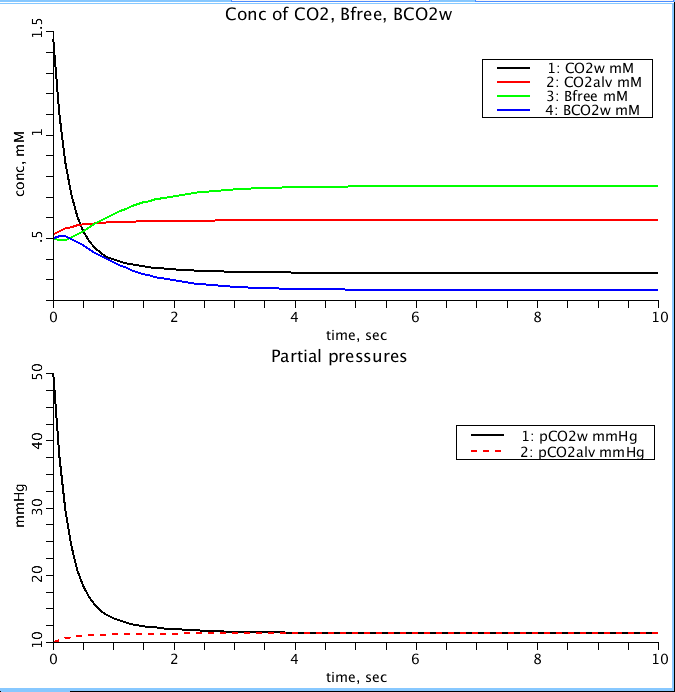
Figure: Concentrations of CO2 in gas and water compartment (Top) as the partial pressures equilibrate between the two (Bottom). Black is CO2 in water compartment, red is CO2 in alveolar gas compartment, green is free binding sites and blue is CO2 bound sites in water compartment. Concentrations in mM and partial pressures in mmHg. Total concentration of binding sites is 1 mM, dissociation constant is 1 mM and kon is 1 (mM*s)^-1.
Equations
The equations for this model may be viewed by running the JSim model applet and clicking on the Source tab at the bottom left of JSim's Run Time graphical user interface. The equations are written in JSim's Mathematical Modeling Language (MML). See the Introduction to MML and the MML Reference Manual. Additional documentation for MML can be found by using the search option at the Physiome home page.
- Download JSim model MML code (text):
- Download translated SBML version of model (if available):
We welcome comments and feedback for this model. Please use the button below to send comments:
Christmas KM and Bassingthwaighte JB. Equations for O2 and CO2 solubilities in saline and plasma: Combining temperature and density dependences. J Appl Physiol 122: 1313-1320, 2017. Dash RK and Bassingthwaighte JB. Erratum to: Blood HbO2 and HbCO2 dissociation curves at varied O2, CO2, pH, 2,3-DPG and Temperature Levels. Ann Biomed Eng 38(4): 1683-1701, DOI: 10.1007/s10439-010-9948-y PMC2862600, 2010 Hills BA, Gas Transfer in the Lung (Book), Cambridge University Press, London, 1974 Comroe J, Lung (Book), YEAR BOOK MEDICAL, Second Edition edition (1965) https://www.imagwiki.nibib.nih.gov/physiome/Models/tutorial
Please cite https://www.imagwiki.nibib.nih.gov/physiome in any publication for which this software is used and send one reprint to the address given below:
The National Simulation Resource, Director J. B. Bassingthwaighte, Department of Bioengineering, University of Washington, Seattle WA 98195-5061.
Model development and archiving support at https://www.imagwiki.nibib.nih.gov/physiome provided by the following grants: NIH U01HL122199 Analyzing the Cardiac Power Grid, 09/15/2015 - 05/31/2020, NIH/NIBIB BE08407 Software Integration, JSim and SBW 6/1/09-5/31/13; NIH/NHLBI T15 HL88516-01 Modeling for Heart, Lung and Blood: From Cell to Organ, 4/1/07-3/31/11; NSF BES-0506477 Adaptive Multi-Scale Model Simulation, 8/15/05-7/31/08; NIH/NHLBI R01 HL073598 Core 3: 3D Imaging and Computer Modeling of the Respiratory Tract, 9/1/04-8/31/09; as well as prior support from NIH/NCRR P41 RR01243 Simulation Resource in Circulatory Mass Transport and Exchange, 12/1/1980-11/30/01 and NIH/NIBIB R01 EB001973 JSim: A Simulation Analysis Platform, 3/1/02-2/28/07.

