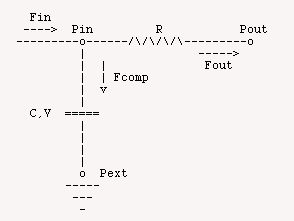
This model uses simulates the flow through a single vessel with resistance to flow R and compliance of the vessel, C, derived from a thin walled formulation of vessel wall mechanics.
Description
This model simulates the flow through, volume of and presssure in a compliant vessel. The compliance of the vessel is based on a thin walled formulation of stress in the vessel wall. A sinusoidal input pressure, Pin drives the flow in the vessel. This simulation employs the fluid analog of a resistive-capacitive electrical circuit where flow, F, is equivalent to electrical current, pressure, P, is equivalent to voltage, compliance, C, is equivalent to electrical capacitance, and resistance to flow, R, is equivalent to electrical resistance. The flows, Fin, Fout and Fcomp, and the vessel volume, V are unknown in this simulation. Therefore the four equations given below are needed to solve for the these unknowns. A three other equations are used to solve for vessel diameter, D, resistance to flow of the vessel, R, and compliance of the vessel, C, based on the thin walled approximation of vessel wall function.
Equations
First we will present the thin walled approximation of stress in a cylindrical vessel wall which is often referred to as the law of Laplace. It is based on the fact that if the cylindrical vessel is divided in half the force in the vessel wall must balance the pressure exerted on the inner surface of the vessel wall. The formulation in terms of stress results in:
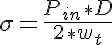
where 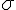
is the circumferential stress in the vessel wall, Pin is the intraluminal pressure at the vessel entrance, D is the vessel diameter and wt is the vessel wall thickness. Assuming a linear stress-strain relationship (Hooke's Law) results in 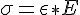
where E is the Young's modulus and 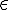
is the vessel wall strain. Assuming that a zero stress state is reached at a non-zero vessel diameter, Dzs, we can expand the linear stress-strain relationship to be:
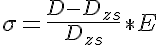
Equating these two expressions and solving for D yields:
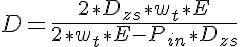
Now since we know that the definition of the compliance is just 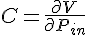
and the vessel volume, V, is specified from the vessel diameter and length, L, we can solve for C:
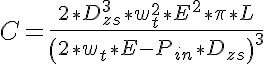
The remaining equations are similar to that of the compliant vessel model. The first equation for flow out of the vessel is related to the resistance by the fluid equivalent of Ohm's Law.
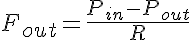
where Pout is the pressure at the outlet of the vessel and R is determined from Poiseuille's Law as:
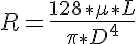
where 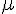
is the fluid viscosity. The flow into the vessel and the flow out of the vessel are different because of the change in volume which adds or subtracts flow from that leaving the vessel depending on whether the pressure is increasing or decreasing in the vessel. So we have:
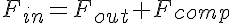
where the flow attributed to the vessel compliance, Fcomp, is given by:
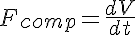
and where V is the vessel volume and is explicitly defined here by the vessel diameter and the length.
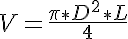
- Download JSim model MML code (text):
- Download translated SBML version of model (if available):
- No SBML translation currently available.
- Information on SBML conversion in JSim
We welcome comments and feedback for this model. Please use the button below to send comments:
Popov EP, Mechanics of Materials, 2nd Edition, 1978, Prentice-Hall Inc. Engelwood, NJ pp 288 - 290.
Please cite https://www.imagwiki.nibib.nih.gov/physiome in any publication for which this software is used and send one reprint to the address given below:
The National Simulation Resource, Director J. B. Bassingthwaighte, Department of Bioengineering, University of Washington, Seattle WA 98195-5061.
Model development and archiving support at https://www.imagwiki.nibib.nih.gov/physiome provided by the following grants: NIH U01HL122199 Analyzing the Cardiac Power Grid, 09/15/2015 - 05/31/2020, NIH/NIBIB BE08407 Software Integration, JSim and SBW 6/1/09-5/31/13; NIH/NHLBI T15 HL88516-01 Modeling for Heart, Lung and Blood: From Cell to Organ, 4/1/07-3/31/11; NSF BES-0506477 Adaptive Multi-Scale Model Simulation, 8/15/05-7/31/08; NIH/NHLBI R01 HL073598 Core 3: 3D Imaging and Computer Modeling of the Respiratory Tract, 9/1/04-8/31/09; as well as prior support from NIH/NCRR P41 RR01243 Simulation Resource in Circulatory Mass Transport and Exchange, 12/1/1980-11/30/01 and NIH/NIBIB R01 EB001973 JSim: A Simulation Analysis Platform, 3/1/02-2/28/07.

